Lung cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally, with its incidence closely linked to smoking, environmental factors, and genetic predisposition. Early detection and advanced treatment methods offer hope, improving survival rates and quality of life for many patients. Here’s what you need to know about lung cancer’s causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Understanding Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is primarily categorized into two types: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC), with NSCLC being more common. The distinction between these types is crucial for determining the most effective treatment strategies.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Smoking: The primary cause of lung cancer, with risk increasing with the duration and number of cigarettes smoked.
- Secondhand Smoke Exposure: Non-smokers exposed to secondhand smoke are at an increased risk.
- Environmental Exposures: Radon gas, asbestos, and air pollution are known risk factors.
- Family History: A family history of lung cancer may increase risk, suggesting a genetic component.
Diagnostic Steps
Early detection of lung cancer can significantly impact treatment success. The diagnostic process involves several steps:
Screening
For high-risk individuals, especially long-term smokers, low-dose CT scans are recommended to detect lung cancer before symptoms appear.
Imaging Tests
Chest X-rays and CT scans are used to identify lung abnormalities. Advanced imaging techniques, like PET scans, may further evaluate lung nodules and check for cancer spread.
Biopsy
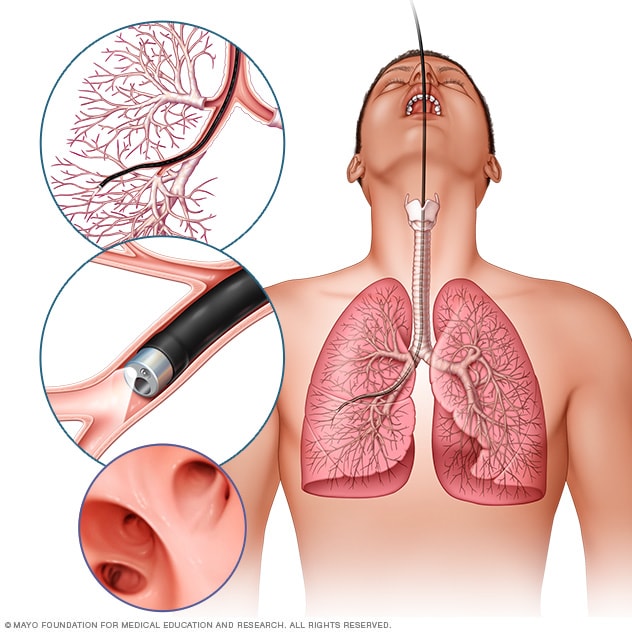
Confirming lung cancer requires a biopsy, where tissue samples from the lung are collected through procedures like bronchoscopy, CT-guided biopsy, or thoracoscopy, and examined under a microscope.
Molecular Testing
Molecular testing of the tumor can identify specific genes, proteins, and other factors unique to the cancer, guiding personalized treatment decisions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for lung cancer depends on the type, stage, and patient’s overall health. Options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, often used in combination for the best outcomes.
Surgery
Surgical options aim to remove the tumor and a margin of healthy tissue. Techniques vary from minimally invasive procedures to more extensive surgeries like lobectomy or pneumonectomy, depending on the tumor’s location and size.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and kill cancer cells. It’s often used after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells or as the primary treatment for those who cannot undergo surgery.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells, usually administered intravenously. It’s often used before surgery to shrink tumors or as a standalone treatment for advanced cancer stages.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy focuses on specific abnormalities within cancer cells. By blocking these abnormalities, targeted drugs can cause cancer cells to die. This approach is particularly effective for cancers with specific genetic mutations.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It’s particularly useful for advanced lung cancer and for patients who haven’t responded to other treatments.
Palliative Care
Palliative care focuses on improving the quality of life for patients with advanced lung cancer, managing symptoms, and providing psychological, social, and logistical support.
Conclusion
Lung cancer, with its complex causes and multiple treatment avenues, requires a comprehensive and personalized approach to care. Advances in diagnostic techniques and treatment strategies offer hope and have significantly improved outcomes for many patients. Early detection through screening, combined with a multidisciplinary treatment approach, is key to managing lung cancer effectively.
For patients and families facing lung cancer, understanding the disease, its diagnosis, and the available treatment options is the first step toward navigating the treatment journey. Collaborating closely with a healthcare team ensures that patients receive tailored care, maximizing their chances for a positive outcome.